News
2025/ 04 / 09
Selection and Considerations for Steelmaking Roll Products
Rolls are critical components in steelmaking and rolling processes, directly affecting rolling efficiency, product quality, and production costs. This article discusses the selection principles and key considerations for rolls used in steelmaking, covering their classification, material selection, operating conditions, and maintenance. The aim is to provide enterprises with guidance for optimizing roll management and improving production efficiency.
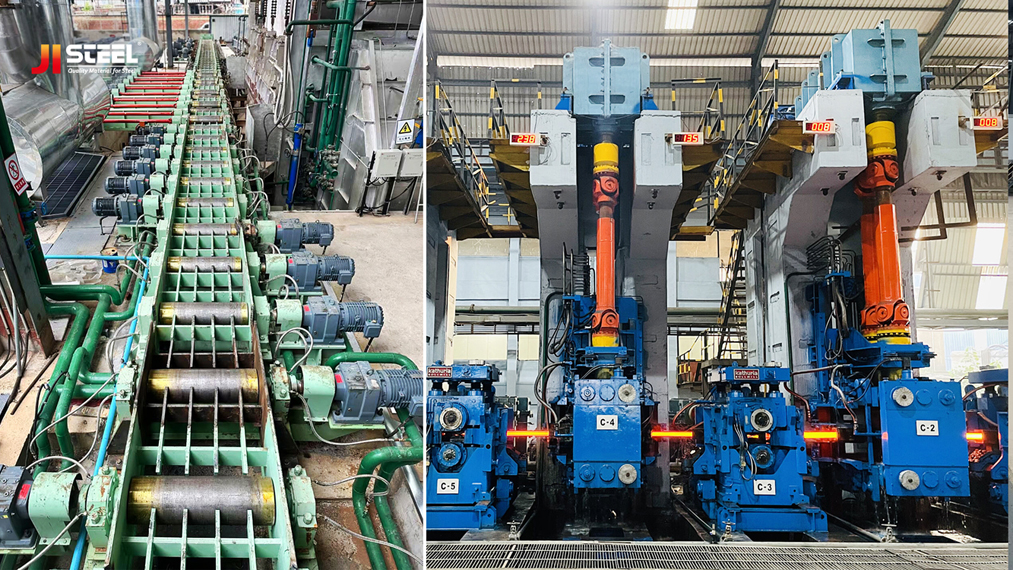

1. Classification and Applications of Rolls
Rolls can be categorized by manufacturing process (cast rolls vs. forged rolls) and by material (cast iron rolls, cast steel rolls, alloy rolls, and composite rolls). Different rolls are suitable for different rolling processes:
Roughing and Intermediate Stands: Typically use high-hardness, high-wear-resistant alloy cast iron or cast steel rolls, such as high-chromium iron (HSS) or high-speed steel rolls, to withstand heavy rolling forces and thermal shock.
Finishing Stands: Require high-precision, high-surface-quality rolls, such as centrifugally cast composite rolls (hard outer layer, tough core) or tungsten carbide rolls, to ensure smooth surface finish on plates or profiles.
Hot Rolling Rolls: Must have excellent thermal fatigue resistance, such as high-nickel-chromium indefinite chilled ductile iron (ICDP) or semi-steel rolls.
Cold Rolling Rolls: Typically use high-carbon high-chromium steel or forged steel rolls to ensure high hardness and wear resistance.
2. Key Factors in Roll Selection
(1) Rolling Process Parameters
Rolling Force: High-load rolling requires high-strength forged or composite rolls.
Rolling Temperature: Hot rolling rolls must resist oxidation, while cold rolling rolls require high hardness.
Rolling Speed: High-speed rolling (e.g., continuous mills) demands rolls with superior thermal crack resistance.
(2) Roll Material and Hardness Matching
Hardness: Roughing rolls typically have a hardness of HS 60-80, while finishing rolls can exceed HS 85.
Toughness: Roughing rolls must balance wear resistance and impact resistance to prevent breakage.
Wear Resistance: High-chromium iron (HSS) and tungsten carbide rolls are suitable for high-wear conditions.
(3) Roll Cooling and Lubrication
In hot rolling, efficient cooling systems are essential to prevent thermal fatigue cracks.
In cold rolling, proper lubricants must be used to minimize wear and extend roll life.
3. Common Issues and Countermeasures in Roll Usage
(1) Surface Spalling and Cracking
Causes: Thermal stress concentration, uneven cooling, or material defects.
Solutions: Optimize cooling systems, select thermal fatigue-resistant materials, and conduct regular nondestructive testing.
(2) Uneven Wear
Causes: Uneven rolling force distribution or roll misalignment.
Solutions: Adjust mill roll gaps, ensure proper roll alignment, and use online roll grinding techniques.
(3) Roll Breakage
Causes: Overloading, internal material defects, or fatigue accumulation.
Solutions: Control rolling parameters, perform regular ultrasonic inspections, and replace aged rolls periodically.
4. Roll Maintenance and Management
Regular Regrinding: Use CNC grinding machines to restore roll surface geometry.
Ultrasonic Testing: Periodically inspect for internal cracks to prevent sudden failures.
Inventory Management: Maintain an optimal roll inventory to avoid production disruptions.
Roll selection and management are crucial for steelmaking and rolling production. Enterprises should choose rolls based on rolling processes, material properties, and operating conditions while implementing effective maintenance strategies to reduce costs and enhance efficiency. In the future, advancements in new materials (e.g., ceramic composite rolls) and smart monitoring technologies will further improve roll performance and longevity.
Contact Us
Address
High-tech Industrial Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China.
jean@ji-steel.com
Phone
+86 188 3804 2177
Products
- Continuous Casting
- ● Copper Mould Tube
- ● Mould Assembly
- ● Ladle And Tundish Nozzle
- Steel Melting
- ● Graphite Electrode
- ● CPC/GPC
- ● Continuous Casting Protecting Slag
- ● Furnace Lining Vibrator
- Rolling Mill Equipment
- ● Steel Roll
- ● Tungsten Carbide Roll Ring
- ● Rolling Mill Guides
- ● Roller Table
Contact
- jean@ji-steel.com
- +86 371 6781 0168
- +86 188 3804 2177
- +86 188 3804 2177
- www.ji-steel.com
- High-tech Industrial Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China.