News
2025/ 04 / 18
Key Equipment in Steel Continuous Casting Process: A Professional Overview
I. Overview of Continuous Casting Process
Continuous Casting (CC) is a core process in modern steel production, directly transforming molten steel into semi-finished products with specific cross-sectional shapes and dimensions, replacing traditional ingot casting and blooming. Since its industrial application in the 1950s, continuous casting has become a critical technology for improving production efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing product quality in steelmaking. The typical CC process includes the following stages: ladle → tundish → mold → secondary cooling → strand withdrawal and straightening → cutting → billet discharge. The entire system relies on the coordinated operation of dozens of specialized equipment components.
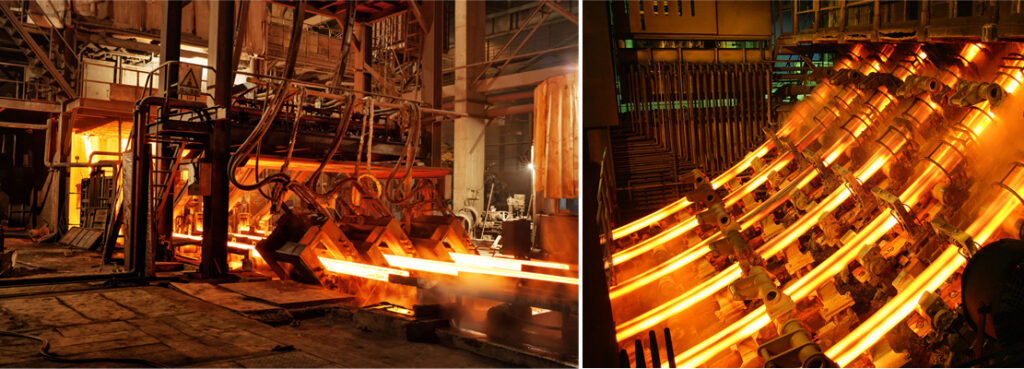
II. Main Equipment in Continuous Casting Systems
1. Molten Steel Transfer and Distribution Equipment
Ladle Turret:
Double-arm or single-arm structure with a load capacity of 300–400 tons
Features lifting (±200 mm), weighing (accuracy ±0.5%), and emergency rotation functions
Key components: hydraulic drive system, segment gear transmission, bearing assembly
Tundish and Car:
Capacity typically 20–30% of the ladle volume, lined with magnesia or alumina-carbon refractory
Equipped with stopper/slide gate dual flow control systems (accuracy ±2 L/min)
Modern tundishes integrate electromagnetic braking, heating (plasma/induction), and other functions
2. Mold System
Copper Mold:
Material: Chromium-zirconium copper (CuCrZr) or silver-copper alloy, thermal conductivity ≥320 W/(m·K)
Taper design: Parabolic or multi-stage to compensate for solidification shrinkage (0.9–1.4%/m)
Oscillation device: Hydraulic or electric servo-driven, non-sinusoidal waveform (frequency 80–400 cpm, amplitude ±3–6 mm)
Electromagnetic Brake (EMBR):
Static magnetic field strength 0.3–0.5 T, effectively controlling steel flow velocity (≤0.3 m/s)
Reduces slag entrainment probability by >50%, especially suitable for high casting speeds (>1.8 m/min)

3. Secondary Cooling System
Zone Spray System:
Typically divided into 6–12 cooling zones, water consumption 0.4–1.2 L/kg steel
Air-mist nozzles (pressure 0.3–0.6 MPa) achieve a water flow adjustment ratio of 1:8
Dynamic water distribution model based on surface temperature feedback (infrared measurement ±15°C accuracy)
Segment Equipment:
Split roller design (roll diameter Φ150–300 mm), support stiffness >50 kN/mm
Features dynamic soft reduction (reduction 0.5–3 mm/m, accuracy ±0.1 mm)
Modern segments integrate roll gap measurement (laser ranging ±0.05 mm), electromagnetic stirring (frequency 2–10 Hz), and other functions
4. Strand Handling Equipment
Withdrawal and Straightening Unit:
Multi-roller arrangement (5–7-point straightening), strain ≤0.2%
Hydraulic servo control, withdrawal speed accuracy ±0.05 m/min
Capable of compression casting to minimize centerline segregation
Flame Cutting Machine:
Multi-torch synchronous cutting (speed adjustment ratio 1:10)
Gas ratio control (propane/oxygen = 1:3.5), kerf loss ≤15 mm
Integrated automatic length measurement system (accuracy ±5 mm)
III. Key Auxiliary Equipment
1. Automation Control System
Level 2 Process Control:
Solidification model (finite difference method, grid size ≤5 mm)
Dynamic secondary cooling algorithm (PID + feedforward control)
Quality prediction system (CQM) accuracy >85%
Sensor Network:
Mold thermal imager (sampling rate 100 Hz, resolution 0.5°C)
Breakout prediction (thermocouple array, warning time >10 s)
Strand surface inspection (CCD camera + laser triangulation)
2. Hydraulic System
Operating pressure 21–28 MPa, flow rate 200–400 L/min
Proportional servo valve response time <10 ms
Accumulator group ensures emergency shutdown energy supply
IV. Technological Development Trends
-
Intelligent Upgrades:
-
Digital twin technology for real-time equipment state mapping
-
AI-driven process parameter self-optimization (e.g., SVM algorithm for oscillation mark control)
-
High-Efficiency, Long-Life Design:
-
Mold copper plate coating lifespan exceeding 20,000 heats
-
Roll stacks using high-niobium steel (Nb >0.08%) or cermet composites
-
Green Innovations:
-
Closed-loop secondary cooling water system (consumption <0.1 m³/t)
-
Waste heat recovery (steam generation 30–50 kg/t billet)
Modern continuous casting equipment is advancing toward “high speed (slab casting >2.5 m/min), high availability (>95%), and high cleanliness ([O] <15 ppm).” The level of equipment integration and intelligence has become a key indicator of steelmakers’ competitiveness. With the deepening application of IoT and big data technologies, continuous casting equipment will transition from “experience-driven” to “data-driven” operations.
Contact Us
Address
High-tech Industrial Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China.
jean@ji-steel.com
Phone
+86 188 3804 2177
Products
- Continuous Casting
- ● Copper Mould Tube
- ● Mould Assembly
- ● Ladle And Tundish Nozzle
- Steel Melting
- ● Graphite Electrode
- ● CPC/GPC
- ● Continuous Casting Protecting Slag
- ● Furnace Lining Vibrator
- Rolling Mill Equipment
- ● Steel Roll
- ● Tungsten Carbide Roll Ring
- ● Rolling Mill Guides
- ● Roller Table
Contact
- jean@ji-steel.com
- +86 371 6781 0168
- +86 188 3804 2177
- +86 188 3804 2177
- www.ji-steel.com
- High-tech Industrial Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China.